This post summarizes the project and the key code/plots from the notebook Data_Preparation_for_Solar_PV_Energy_Prediction_with_LSTM_V.ipynb.
TL;DR
- Performed DBSCAN-based outlier cleaning and targeted feature engineering (cyclical time features and sunrise-offsets) to improve forecasting signal quality.
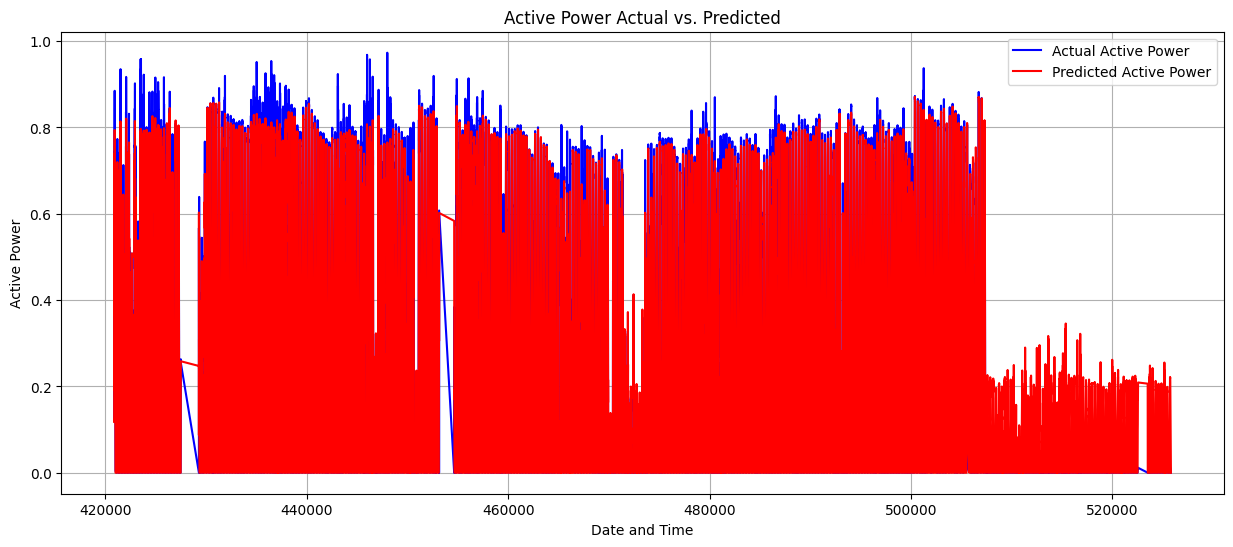
- Built and trained a custom LSTM variant in PyTorch for multivariate time-series forecasting and evaluated performance on held-out data.
What this post contains
- Short project overview
- Datasets used
- Key preprocessing & feature engineering steps
- Outlier detection and handling strategy
- Model summary and training notes
Datasets
PV_Array_4.csv— primary PV array time-series (power, irradiance, weather features, timestamp parts)sunrise_sunset_data_2024.csv— daily sunrise and sunset timestamps used to restrict analysis to daylight hours
Data provenance: The datasets contain real measurements collected from solar panels installed at my school (not synthetic or simulated).
Both datasets are originally downloaded inside the notebook (via gdown), then loaded with pandas.read_csv.
Key preprocessing steps
- Compose a single datetime column and align the two data sources via an as-of merge.
- Reindex to a uniform time grid (5-minute frequency) and filter to daytime points using sunrise/sunset.
- Detect and treat outliers in the (irradiance, power) space using DBSCAN, then project outliers onto a smoothed, monotonic mean curve built with isotonic regression + interpolation.
- Engineer cyclical time features (sine/cosine for hour and month) and an elapsed-time-since-sunrise feature.
- Normalize numeric features before sequence building.
Outlier handling (short)
- DBSCAN is used to separate normal operating points from rare/noisy points.
- Identified outliers are projected onto a physics-informed monotonic mapping (irradiance → expected power) via isotonic regression and interpolation, preserving the physical monotonic relationship between irradiance and power.
Model (summary)
- Custom 2-layer LSTM variant implemented in PyTorch.
- Trained for forecasting Active Power from multivariate inputs (irradiance, temperature, humidity, rainfall, time features).
- Standard training loop with MSE loss and early stopping on validation loss.
Results / Evaluation metrics
- Mean Squared Error (MSE): 0.0050
- Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE): 0.0708
- Mean Absolute Error (MAE): 0.0388